

Choppy - An erratic pattern of higher highs and lower lows.Although this progress can move many points over a short period of time, it often results in very little net price movement over time. Trendless - Erratic price movements that are often steep ( greater than a 45-degree angle) and cannot be sustained, so must reverse.Down-trends - A pattern of lower lows and lower highs.Up-trends - A pattern of higher highs and higher lows.Trending - Steady elongated price movements with less than a 45-degree angle, with occasional pauses, profit taking or rest periods.These market types and patterns can be defined as follows: Each market type has two specific patterns, which you will also come to recognise over time. There are two types of market that become important for the beginner trader to identify: trending and trendless. Once a pattern is established, it becomes the most probable course of future price action until the market changes. The market often displays some very familiar patterns of price movement. The small dot on the right-hand side represents the period's closing price. Regular bars display a small dot on the left-hand side of the bar representing the opening price of the period. The lowest point of the bar represents the lowest price during the same period. Firstly, the highest point of the bar represents the highest price achieved during that time period. Each bar has similar characteristics and gives the viewer several important pieces of information. For example, we use one-minute and five-minute bars in our system. They enable the viewer to see a graphical representation summarising the activity within a specified time frame. Price bars are a linear representation of a period of time. Tr = Volume or number of trades (not contracts) in that time period. Most computer programs will display a small box of data, usually called a display window, which will contain the following items:

Therefore, by studying the price charts, you are indirectly seeing fundamental and market psychology simultaneously - after all the market is fed by two emotions - greed and fear - and once you understand that, then you begin to understand the psychology of the market and how it relates to the chart patterns. Thus, all fundamental factors are quickly discounted in price. It is the urgency between buyers and sellers in the trading pit that creates price movement. Price reflects the perceptions and action taken by the market participants. Divergence between the stochastic lines and the price action of the underlying instrument gives a powerful trading signal. Stochastic calculations produce two lines, %K and %D, which are used to indicate overbought/oversold areas of a chart. Conversely, as prices fall in a b down trend, closing prices tend to be near to the extreme low of the period range. The indicator is based on the observation that in a b up trend, closing prices for periods tend to concentrate in the higher part of the period’s range. This is used to indicate overbought/oversold conditions on a scale of 0-100%. An RSI of 30 or less is taken as a signal that the instrument may be oversold (a situation whereby prices have fallen more than market expectations). If the RSI is 70 or greater, then the instrument is seen as overbought (a situation whereby prices have risen more than market expectations). The RSI measures the ratio of up moves to down moves and normalises the calculation so that the index is expressed with a range of 0-100. This index is a popular indicator of the Forex (FX) market.
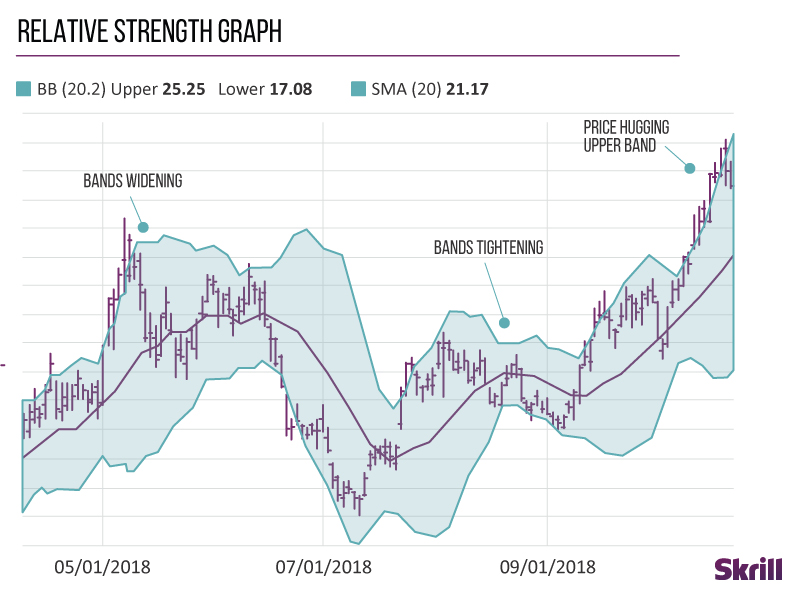
Below are just a few basic points to help your understanding of technical analysis and currency chart reading. To be profitable in today's world of technology and advancement, one must be proficient in reading and, more importantly, understanding chart patterns and basic technical indicators.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
